Menu
close
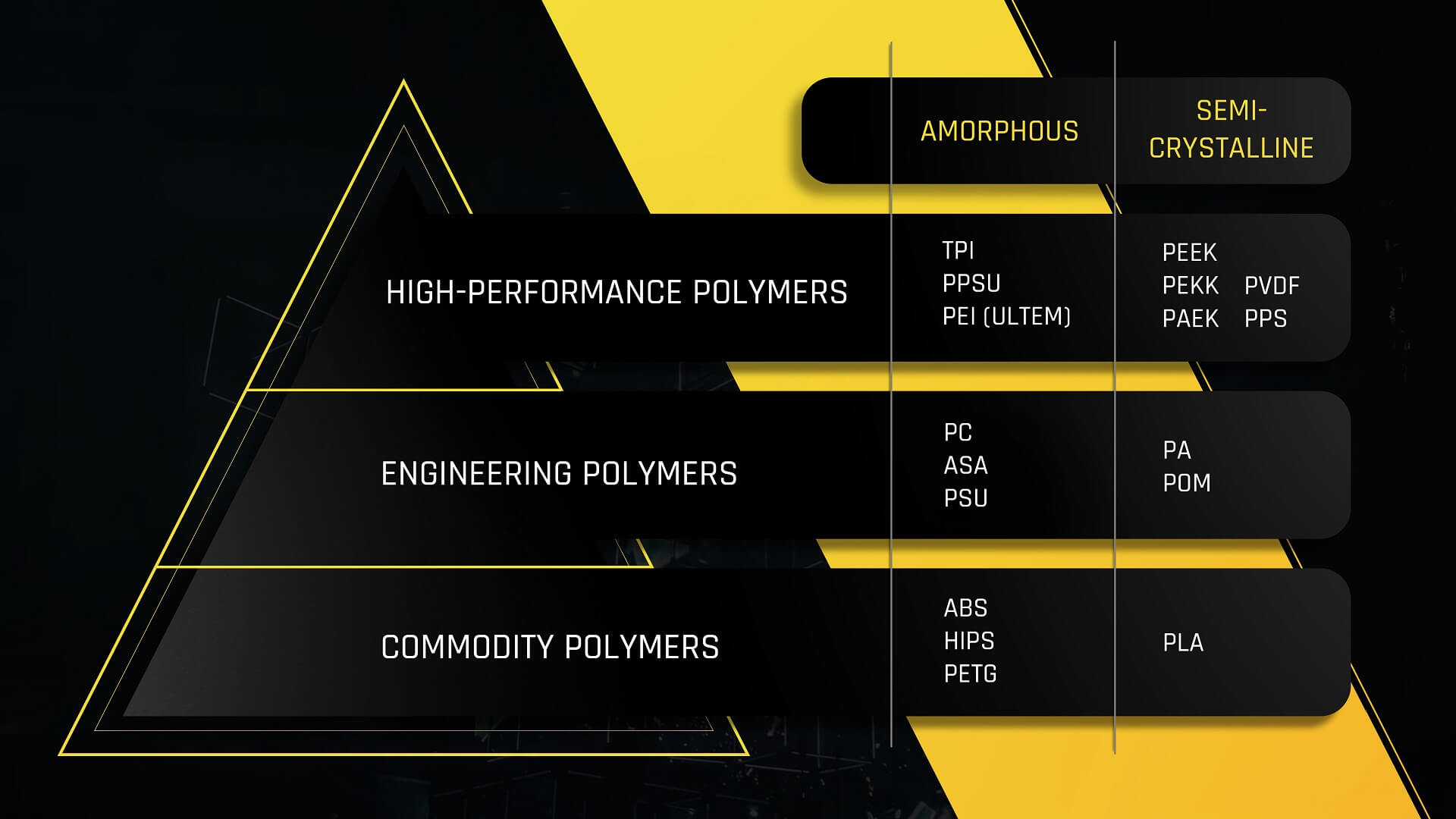
Ultra polymers, high-performance polymers, super polymers, specialty polymers, whatever you want to call them, can be found at the top of the polymer pyramid. These materials have significantly higher performance than traditional engineering polymers and are often referred to as metal replacement applications in the context of ultra polymers, where the properties of the materials shine. 3D printing of ultra polymers is a relatively new thing that has become possible thanks to the high-performance miniFactory Industrial 3D Printers. The Ultra 2 3D printer has been developed for 3D printing of ultra polymers and the 250°C-heated printing chamber of the device enables the best possible quality of printed high-performance polymer parts.
The most significant properties of ultra polymers are related to applications that combine high operating temperatures of up to 250°C with corrosive or strong chemicals. Another major use is in the metal replacement applications. Metal is durable, but it is also heavy, expensive, and corrodes over time. New solutions are needed in many industries where metal just isn’t an option anymore.

The extreme chemical resistance of high-performance polymers allows their utilisation in environments where metals are often oxidised or rusted. High-performance polymers offer long-term reliability and shorten downtime due to their excellent resistance to strong chemicals and solvents in even the most challenging environments and applications.
Metals require various expensive finishes and coatings in order to be used in similar environments. If metal parts are scratched or the coating wears off, the chemicals will easily start to corrode them. This leads to the loss of material beginning with the surface and also loss of mechanical properties. With plastic, these treatments are not needed.
High-performance polymers have extreme chemical resistance to acids, alcohols, fuels, oils, and halogenated solvents. It makes them an ideal material for use in situations where precision fluid handling components in the chemical and processing industries are needed.
Industries are constantly looking for strong and lightweight materials that make it possible to simplify the design of parts, reduce system costs, and provide more durability in parts exposed to harsh conditions.
By utilising high-performance polymers instead of metals, products can be made significantly lighter than before. High-performance polymers provide better fuel efficiency and improved durability thanks to their light weight.
Polymers are up to six times lighter than many metals. Thus, for example, companies in aerospace or space can make significant savings in fuel costs by replacing metal parts with high-performance polymers.
Traditional engineering plastics have become accustomed to certain limitations in terms of operating environments and, above all, operating temperatures. Where the most common engineering polymers can withstand operating temperatures up to about 100°C, high-performance polymers allow operating temperatures up to over 250°C.
In many applications, plastic would have been the perfect solution if the operating temperature had been higher. Until now, the industry has opted for metal parts that are heavy, expensive, and have a poor service life in applications that are unsuitable for metals. With 3D printing of ultra polymers, the time for compromise is over, and the right high-performance polymer can be selected for the application. For example, there are countless applications in process manufacturing, from heat treatment environments to the curing stages of painting lines. In these applications, the high-performance polymer 3D printing provides a cost-effective and optimal solution that allows for significant savings.
High-performance polymers have shown great electrical insulation properties as well as enhanced thermal performances. Excellent insulation is a must for power generation equipment that deals with electrical currents. When insulation is combined with a high temperature resistance, even above 250°C, the applications of the materials multiply rapidly. As transport vehicles become more electric and lighter, more durable and safer materials are sought. High-performance polymers are resistant to electron flow because of the low number of subatomic particles. This prevents electrical charges from freely transiting through the body.
Metal materials often require expensive finishes and coatings to achieve even some level of insulating properties. However, even the treated metal does not have the same properties as a polymer.
High-performance polymers withstand friction and wear well, making them an excellent solution for demanding applications. The low coefficient of friction allows the use of polymer components in dry conditions. Lubricants are also unnecessary. By using polymers instead of metals, you can ensure long-lasting, low noise and low vibration parts.
Lubricants are essential in all metal-to-metal contacts. Even if lubricants are added regularly and thus an optimal operating environment is maintained, metals still wear out faster than plastics in use. High-performance polymers are an excellent option for mechanical engineering applications, as parts can be complex in shape and mainly present great tribological performance. Self-lubricating properties extend component life and reduce maintenance.
Plastics used in the medical and food industries, among others, must be sterilisable. This ensures a high level of operational safety without affecting their performance. Polymers present good cleaning and sterilisation properties, which makes them a good solution for demanding applications. The cleanliness of tools and utilities used in the medical industry is vital. Infections are one of the biggest threats patients face in hospitals. It can be easily avoided by using equipment that can be properly sterilised.
In the food production industry, sterilisation is an often-repetitive operation. It is very important that the sterilisation process does not affect the durability of parts used in production. High-performance polymers like PPSU or ULTEM1010 can endure repeated sterilisation cycles. In particular, they can stand up to harsh methods like chemical, steam, or radiation sterilisation without significant damage.
Most ultra polymers are classified according to the UL94 V-0 fire classification. UL94 is one of the most widely used flammability tests for determining relative flammability for plastic materials. Thus, the materials have good fire ratings, allowing them to be used in more challenging applications.
In addition to the UL94 V-0 classification, some materials have other, industry-specific approvals. For example, the ULTEM9085 resin meets aviation standards by being FST compliant with an OSU rating of 55/55. ULTEM9085 resin and PEKK meet the EN45545-2 standard of the railway industry. Both special standards relate to the ignition of materials and the formation of toxic gases.
Materials such as ULTEM1010 or PC-S have a food contact certification EU 10/2011, FDA 21 CFR, which makes it possible to use the materials in food applications. Thus, it can be said that ultra polymers live up to their name and materials can be utilised in the most challenging applications.
Contact us and our specialists will be in touch shortly.
"*" indicates required fields